They say the difference between a dream and a goal is a timeline. But once you have a goal and a timeline, you need a way to measure your progress. In the language learning world, Cambridge Assessment English does this using the Common European Framework for Reference (CEFR) in its exams. On the other side of the pond, the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) has its own framework, ACTFL. But what is ACTFL Foreign Language Assessment? ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines differ from CEFR’s, so it’s essential to know how your language or your student’s language skills are going to be measured.

What Is ACTFL?
ACTFL stands for the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages, a membership organisation founded by and for language professionals in 1967. Its aim is to expand cultural richness, provide resources, publications and professional development to language teachers, conduct innovative research, and offer language assessment to students.
Every year, ACTFL administers more than 700,000 exams in more than 60 countries in over 120 languages. These assessments are used globally by government agencies, private corporations and academic institutions for programme evaluation, professional certification, hiring, promotion and academic placement.
How Does ACTFL Assess Languages?
ACTFL assesses language proficiency using a scale called Proficiency Guidelines, which describes levels of language proficiency across the four main communication skills: speaking, listening, reading and writing.
What Is ACTFL Proficiency?
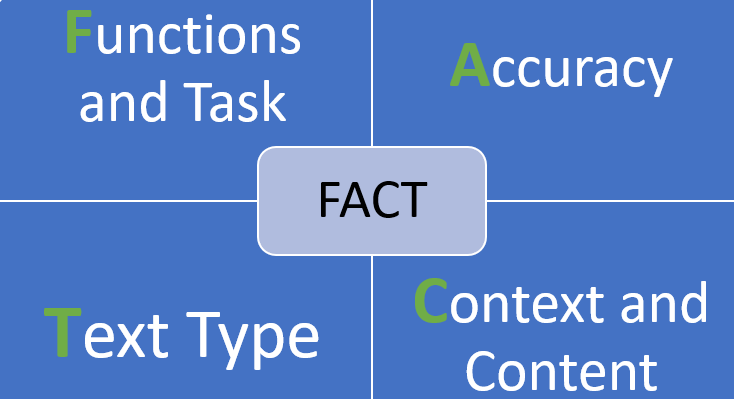
An individual’s proficiency in each category is defined by four criteria, which can be remembered using the acronym FACT:
- functions and tasks
- accuracy
- context and content
- and text type
Functions and tasks refers to the types of activities in which students are competent, from introducing themselves, following instructions, expressing feelings to negotiating. Accuracy is how well a student uses the linguistic features of a language, such as the present perfect, for example. Context and content looks at the various topics a student can communicate and in what situations. Text type refers to the oral or written text length and complexity that a student can understand or produce.
Modes Of Communication
For each category, the guidelines also reference three modes of communication: interpretive, interpersonal, and presentational.
Interpretive mode is about one-way communication, such as listening to the radio or a podcast. It could also be reading a blog post or book. Interpersonal is about speaker interaction and could involve emails or video calls. Presentational is about one-way communication and presentation. It could involve giving instructions or recording a video or written message.
Proficiency Vs Performance
The ACTFL defines proficiency and performance differently. Proficiency is defined as the ability to communicate in any situation without previous preparation or rehearsal on the topic or context, both of which could be new to the student. Performance is the opposite. Students will be graded on their ability to perform specific communication tasks that can be rehearsed or prepared, using task-oriented language vocabulary and structures familiar to them.
Performance grading affects the major level but not the sublevel of a student’s final grade. Furthermore, it does not extend to the two highest grades, superior and distinguished.
What Grades Can You Get?
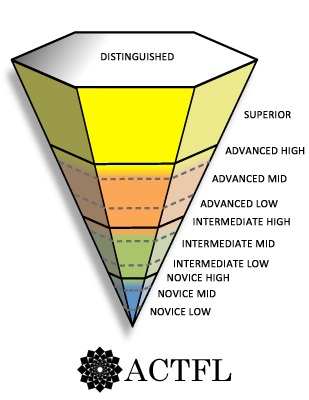
Language learners taking ACTFL assessments can achieve several different results, as there are five major levels and some sublevels. The five major levels are:
- novice
- intermediate
- advanced
- superior
- and distinguished
At novice, intermediate and advanced levels it’s possible to score one of three sublevels: low, mid, and high. This allows students to see how close they are to reaching the next major level while also highlighting their ability within their current level.
What Are ACTFL Can-do Statements?
“Can do statements ACTFL?”, “FACT”, and “Proficiency vs Performance”? When it comes to language assessment, there is no shortage of jargon and acronyms to remember. But Can-do Statements are a way of simplifying communication between ACTFL, teachers and language students. The statements are designed to:
- help language learners set goals and chart their progress towards proficiency
- guide educators on how to communicate learning targets at the lesson, unit and curriculum level
- and show stakeholders how learners at different stages of their journey can communicate
ACTFL calls a student’s ability to use their target language their Intercultural Communicative Competence (ICC), which can be tracked at the novice through to distinguished stages by using Can-do Statements. These statements are aligned with the previously mentioned Proficiency Guidelines and Performance Descriptors.
How Are Can-do Statements Organised?
Can-do Statements are organised according to the three Modes of Communication mentioned earlier: interpretive communication, interpersonal communication, and presentational communication. Learners may be at different levels or sublevels for each mode, but Can-do Statements can still be used to measure proficiency using clear benchmarks and examples. They are not a checklist that, once completed, suggests a skill is mastered or offers a grade. They are indicators of a student’s language journey, allowing goals to be set and their progress to be monitored.
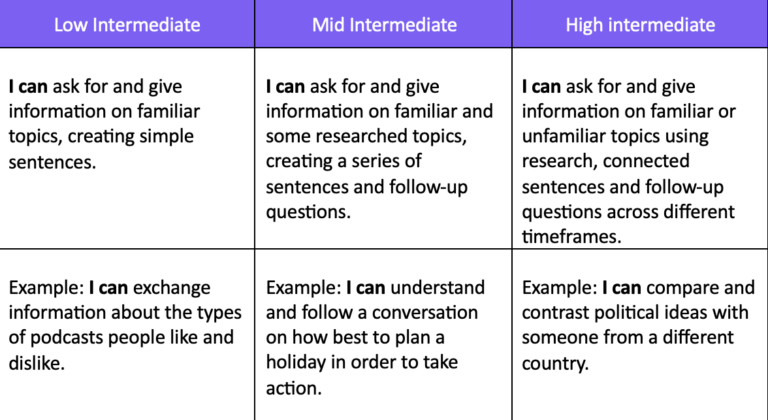
Here is an example of how ATCFL might assess the low and high intermediate sublevels of a speaking test using performance indicators and Can-do Statements:
What Is ACTFL Foreign Language Assessment?
In summary, ACTFL is an American organisation focusing on the teaching and learning of all languages with over 13,000 members, from elementary to graduate education, working in schools, government and elsewhere. ACTFL standards and ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines create a coherent grading system for assessing language. This includes the four criteria acronymized as FACT, Modes of Communication, and Can-do Statements that allow teachers and students to plan, set progress goals and assess tests.
Did you know you can find out the ACTFL levels of your reading materials or videos using Cathoven’s ACTFL Analyzer?
What next?
Now that you know one method of measuring language progress, you’re one step closer to making your language goals a reality, not just a dream. However, there is more than one way to assess language. Other organisations, such as Cambridge Assessment English, have their own guidelines and methods for assessing language proficiency.
Interested in our blog Comparing ACTFL, the American Standard, with CEFR, the European Standard? – Read here!
