Why teachers often need to change the Lexile Level of a text
Teachers all know that there is often a wide range of student reading ability in nearly every classroom. Thus, if a teacher really wants to help all of their students to make progress, she needs a means to find, or create, texts which appropriately challenge her students, without overwhelming them.
Traditionally, teachers looked to Lexile Levels to help find materials appropriate for their students. Thus, first, let’s take a look at the Lexile Level system, and why it has been used for so many years as the best means to determine the difficulty level of reading material for students.
Then, we’ll examine Catile, a new, more modern, in-depth approach for determining the level of difficulty for any given text, along with a new, efficient way to easily change the Lexile Level of a text.
What are Lexile Levels and Why are they important?

For many years, Lexile levels have been considered to the be the most accurate measurement of the difficulty of a text, and they have most often been used to determine the suitability of school textbooks for specific grade levels.
The Lexile system was developed by MetaMetrics, and their goal was to create a framework for reading by creating a research-based, scientific system to determine the level of a text so that teachers and school administrators would have the information they needed to select appropriate textbooks for their classrooms.
According to the Lexile website:
The Lexile Analyzer measures the complexity of the text by analyzing characteristics such as sentence length and word frequency. Generally, longer sentences and words of lower frequency lead to higher Lexile measures; shorter sentences and words of higher frequency lead to lower Lexile measures.
Lexile.com
After analyzing sentence length and word frequency in a text, the Lexile system then assigns a level of difficulty between 0L, for beginning readers, to over 2000L, for very advanced readers.
This system proved to be very useful for teachers as Lexile also developed a Lexile chart which indicated typical Lexile reading ability for different US grade levels, so teachers were able to identify materials appropriate for the grade-level which they were teaching.
The company also states that, of course, there will be a range of reading ability in any given classroom, which means that in order to provide appropriate materials for all of their students, a teacher may need to differentiate reading materials for different students in a given class, meaning that teachers are faced with the task of how to change the Lexile Level of a text
What is Catile and how does it differ from Lexile?
As we describe above, the Lexile system measures sentence length and word frequency as the primary characteristics to determine the difiiculty of a text, and for many years, this was the gold standard in measuring the difficulty and complexity of materials for the classroom.
However, Cathoven, a company which is comprised of both language teachers and AI engineers, has harnessed the power of AI to create a more accurate tool to analyze the difficulty of any text.
While Lexile uses two basic parameters, sentence length and word frequency, to determine the difficulty level of a text, Cathoven’s Catile system assigns a Catile score, which assesses text difficulty through a detailed analysis focusing on four main areas: decoding ease, vocabulary familiarity, sentence complexity, and repetition patterns.
Cathoven describes how their system produces a Catile score:
Catile leverages artificial intelligence, specifically Natural Language Processing (NLP), to process the text and extract different aspects like decoding ease, vocabulary familiarity, sentence complexity, repetition patterns, and so on. The innovation behind Catile lies in its ability to dig into subtleties of language use, distinguishing between structures and words based on their grammatical roles and contextual meanings.
Cathoven.com
How do I convert a Catile score into a Lexile Level?
Now that we see that Catile is a more accurate way to measure the difficulty of a text, we also need to know that it is very easy to convert a Catile score to a Lexile Level.
Cathoven adopted a similar grading scale with Lexile and used it as their benchmark, so you can expect the Catile score of a passage to be very close to the corresponding Lexile Level. For example, a 1050 Catile Score = a 1050 Lexile Level.
This can be important as many standard tests for students provide Lexile Levels, so one can use the Catile Analyzer to check the level of any text to determine the Lexile Level, with the added bonus of getting more detailed information about a given text from the Catile Analyzer than you would have with a Lexile Level.
What information does a Catile score provide?
When using the Catile Analyzer, it is very easy to determine the Lexile Level of a text. In the sample below, I used the Catile Analyzer to determine the level of a news article which I wanted to use with students.
You can see that the text has a Catile Score of 1020C, which means the Lexile Level is also 1020L. However, with the Catile Analyzer, we are also given additional information.
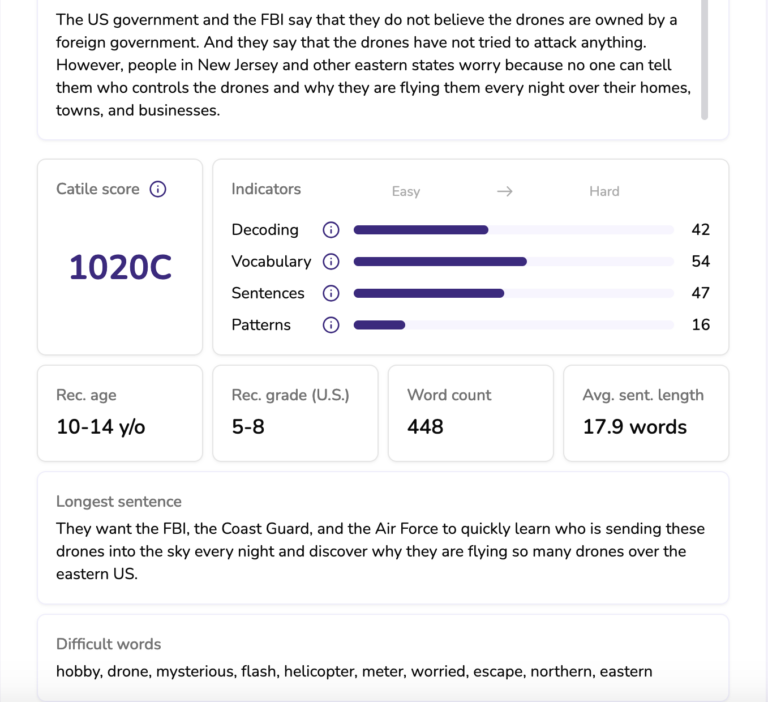
The Catile Analyzer also tells us the recommended age level which the text may be used with, in this case, ages 10-14; it gives us a range for the recommended grade level, US 5-8, and it provides us a list of the words in the text which are considered difficult at this level.
Finally, we also find the four indicators which are used to determine the level of difficulty of the text, and a breakdown for how each category affects the Catile, and Lexile, score for the text:
- Decoding: Easier texts have words with fewer syllables and simpler sounds (e.g., “net” and “shop”).
Harder texts have words with more syllables and more complex sounds (e.g., “balloon” and “ceremony”).
- Vocabulary: Easier texts have more common, familiar and concrete words.
Harder texts have more rare, unfamiliar and abstract words.
- Sentences: Easier texts have shorter sentences and more words that overlap between sentences.
Harder texts have longer sentences and fewer words that overlap between sentences.
- Patterns: Easier texts have more repeated words and phrases.
Harder texts have fewer repeated words and phrases.
In this example, the Catile Analyzer has indicated that the level of difficulty for Decoding, Vocabulary, and Sentence length are similar, while the Patterns in the text are easier; thus, if I am using the text to recycle a lot of vocabulary or to reinforce specific information, I have likely achieved my goal, as the Catile Analyzer has found more repeated words and phrases in the text.
How to change the Lexile Level of a text
For this example, let’s imagine that we are teaching a 9th grade US high school Social Studies class, World History. In our textbook, we have a long section on the Italian Renaissance, and we know that many of our students may be completely unfamiliar with the material. And we also know that quite a few of our students are reading at two or more levels below the 9th grade level.
This unit is part of our required curriculum, so what are we going to do?
First, we can assess the difficulty of the text we have for this unit. We can simply paste or type the text into the Catile Analyzer and discover the level of difficulty of the text.

Here, we see that the text we are working with has a Catile Score of 1100, which is equivelent to a Lexile Level of 1100L, and we can see that the first two of the metrics, Decoding and Vocabulary, are on the upper-end of the scale of difficulty, so with a number of students in class reading below grade level, we know that we need to adapt this material, perhaps as a pre-reading exercise, to provide additional support for some students.
How to change the Lexile Level of a text: the Cathoven Level Adapter
Now that we have determined the level of our text, we can simply move over to the Cathoven Level Adapter, copy and paste our text from the Analyzer into the Adapter, and decide which target metric we want to use to adapt our text.
The Cathoven Level Adapter gives us the option to change the text to a Catile/Lexile level, US Grade Level, or Age Level. For English as a Foreign Language teachers, one can also adapt a text for a specific CEFR level.
Since I know that I have some students reading significantly below Grade Level, I decide to change the Catile/Lexile Level of the text from 1100 to 800, a significant decrease in reading difficulty.
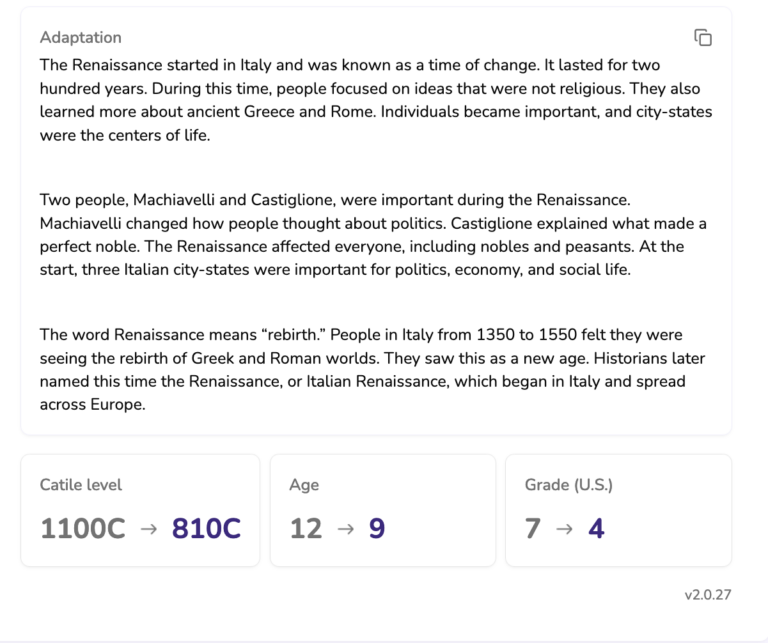
As you can see, the Cathoven Level Adapter was able to quickly change the Catile, or Lexile Level, of a text from 1100 to 810, a decrease of almost 300 points, so if I give my lower-level students an adapted text as a pre-reading activity, before we get to the textbook, they are likely to have a much better chance at comprehending the lesson.
Final thoughts on how to change the Lexile Level of a text
Almost all teachers are faced with a range of reading ability within their classrooms, and this challenge is often compounded by the assignment of mandatory textbooks and other materials; thus, the question is always: “how do I provide support so that all of my students can make progress and learn?”
As we have discussed, the first step is to analyze the text you plan to use with students and get an accurate assessment of its level of difficulty. Cathoven’s language teaching experts and AI engineers have developed the Catile Analyzer which provides the easiest, most accurate way to determine the Catile, and Lexile Level, of any text.
Next, once you know the level of your material, you can move on to the Cathoven Level Adapter to quickly and easily change the Lexile Level of a text. In this way, you can offer reading materials at different levels to meet the diverse needs of students in your classes.
Best of all, it is completely free to try out these cutting-edge AI tools for assessing and adapting reading materials. Check out these tools and several others at Cathoven today!
